Page 47 - ICC Science Dictionary (spreads)
P. 47
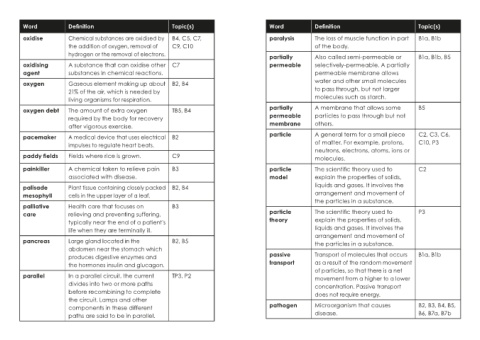
Word Definition Topic(s) Word Definition Topic(s)
oxidise Chemical substances are oxidised by B4, C5, C7, paralysis The loss of muscle function in part B1a, B1b
the addition of oxygen, removal of C9, C10 of the body.
hydrogen or the removal of electrons. partially Also called semi-permeable or B1a, B1b, B5
oxidising A substance that can oxidise other C7 permeable selectively-permeable. A partially
agent substances in chemical reactions. permeable membrane allows
oxygen Gaseous element making up about B2, B4 water and other small molecules
21% of the air, which is needed by to pass through, but not larger
living organisms for respiration. molecules such as starch.
oxygen debt The amount of extra oxygen TB5, B4 partially A membrane that allows some B5
required by the body for recovery permeable particles to pass through but not
after vigorous exercise. membrane others.
pacemaker A medical device that uses electrical B2 particle A general term for a small piece C2, C3, C6,
impulses to regulate heart beats. of matter. For example, protons, C10, P3
neutrons, electrons, atoms, ions or
paddy fields Fields where rice is grown. C9 molecules.
painkiller A chemical taken to relieve pain B3 particle The scientific theory used to C2
associated with disease. model explain the properties of solids,
palisade Plant tissue containing closely packed B2, B4 liquids and gases. It involves the
mesophyll cells in the upper layer of a leaf. arrangement and movement of
the particles in a substance.
palliative Health care that focuses on B3
care relieving and preventing suffering, particle The scientific theory used to P3
typically near the end of a patient's theory explain the properties of solids,
life when they are terminally ill. liquids and gases. It involves the
arrangement and movement of
pancreas Large gland located in the B2, B5 the particles in a substance.
abdomen near the stomach which
produces digestive enzymes and passive Transport of molecules that occurs B1a, B1b
the hormones insulin and glucagon. transport as a result of the random movement
of particles, so that there is a net
parallel In a parallel circuit, the current TP3, P2 movement from a higher to a lower
divides into two or more paths concentration. Passive transport
before recombining to complete does not require energy.
the circuit. Lamps and other
components in these different pathogen Microorganism that causes B2, B3, B4, B5,
paths are said to be in parallel. disease. B6, B7a, B7b