Page 24 - ICC Science Dictionary (spreads)
P. 24
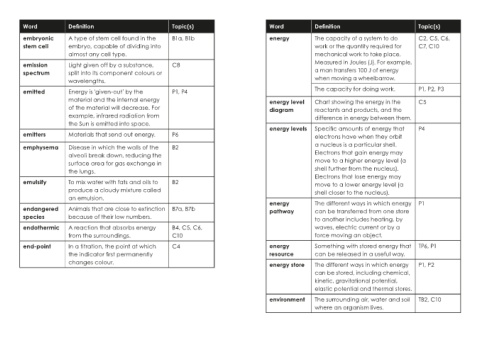
Word Definition Topic(s) Word Definition Topic(s)
embryonic A type of stem cell found in the B1a, B1b energy The capacity of a system to do C2, C5, C6,
stem cell embryo, capable of dividing into work or the quantity required for C7, C10
almost any cell type. mechanical work to take place.
emission Light given off by a substance, C8 Measured in Joules (J). For example,
spectrum split into its component colours or a man transfers 100 J of energy
wavelengths. when moving a wheelbarrow.
emitted Energy is 'given-out' by the P1, P4 The capacity for doing work. P1, P2, P3
material and the internal energy energy level Chart showing the energy in the C5
of the material will decrease. For diagram reactants and products, and the
example, infrared radiation from difference in energy between them.
the Sun is emitted into space.
energy levels Specific amounts of energy that P4
emitters Materials that send out energy. P6 electrons have when they orbit
emphysema Disease in which the walls of the B2 a nucleus is a particular shell.
alveoli break down, reducing the Electrons that gain energy may
surface area for gas exchange in move to a higher energy level (a
the lungs. shell further from the nucleus).
Electrons that lose energy may
emulsify To mix water with fats and oils to B2 move to a lower energy level (a
produce a cloudy mixture called shell closer to the nucleus).
an emulsion.
energy The different ways in which energy P1
endangered Animals that are close to extinction B7a, B7b pathway can be transferred from one store
species because of their low numbers. to another includes heating, by
endothermic A reaction that absorbs energy B4, C5, C6, waves, electric current or by a
from the surroundings. C10 force moving an object.
end-point In a titration, the point at which C4 energy Something with stored energy that TP6, P1
the indicator first permanently resource can be released in a useful way.
changes colour. energy store The different ways in which energy P1, P2
can be stored, including chemical,
kinetic, gravitational potential,
elastic potential and thermal stores.
environment The surrounding air, water and soil TB2, C10
where an organism lives.