Page 31 - ICC Science Dictionary (spreads)
P. 31
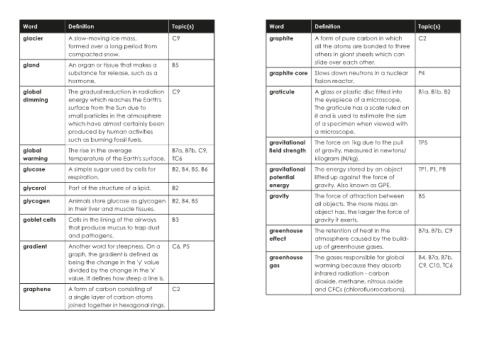
Word Definition Topic(s) Word Definition Topic(s)
glacier A slow-moving ice mass, C9 graphite A form of pure carbon in which C2
formed over a long period from all the atoms are bonded to three
compacted snow. others in giant sheets which can
gland An organ or tissue that makes a B5 slide over each other.
substance for release, such as a graphite core Slows down neutrons in a nuclear P4
hormone. fission reactor.
global The gradual reduction in radiation C9 graticule A glass or plastic disc fitted into B1a, B1b, B2
dimming energy which reaches the Earth's the eyepiece of a microscope.
surface from the Sun due to The graticule has a scale ruled on
small particles in the atmosphere it and is used to estimate the size
which have almost certainly been of a specimen when viewed with
produced by human activities a microscope.
such as burning fossil fuels. gravitational The force on 1kg due to the pull TP5
global The rise in the average B7a, B7b, C9, field strength of gravity, measured in newtons/
warming temperature of the Earth's surface. TC6 kilogram (N/kg).
glucose A simple sugar used by cells for B2, B4, B5, B6 gravitational The energy stored by an object TP1, P1, P8
respiration. potential lifted up against the force of
glycerol Part of the structure of a lipid. B2 energy gravity. Also known as GPE.
gravity The force of attraction between B5
glycogen Animals store glucose as glycogen B2, B4, B5 all objects. The more mass an
in their liver and muscle tissues.
object has, the larger the force of
goblet cells Cells in the lining of the airways B3 gravity it exerts.
that produce mucus to trap dust greenhouse The retention of heat in the B7a, B7b, C9
and pathogens. effect atmosphere caused by the build-
gradient Another word for steepness. On a C6, P5 up of greenhouse gases.
graph, the gradient is defined as greenhouse The gases responsible for global B4, B7a, B7b,
being the change in the 'y' value gas warming because they absorb C9, C10, TC6
divided by the change in the 'x' infrared radiation - carbon
value. It defines how steep a line is. dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide
graphene A form of carbon consisting of C2 and CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons).
a single layer of carbon atoms
joined together in hexagonal rings.